The Rare Occurrence of a Single Transaction in a Block
Ethereum's block structure is notoriously complex, with each block containing multiple transactions and data. However, every 10 minutes, a new block is mined on the Ethereum network, containing one or more transactions as well as other important data such as the block number, timestamp, and nonce.
However, in some cases, a block may contain only one transaction. This phenomenon has been observed in several instances, and it is essential to understand what causes this rare occurrence.
Why Does a Single Transaction Occur?
There are several reasons why a block may contain only one transaction:
Transaction Fees: If the network is congested with high-value transactions, the block miner may choose to include only one transaction instead of several smaller transactions. This reduces the computational cost associated with processing the data and ensures that the mining process does not consume too many resources.
Economic Constraints: In some cases, a single transaction may be more beneficial to the sender than a series of transactions, especially if the recipient is willing to accept only one payment or has limited funds.
Network Congestion: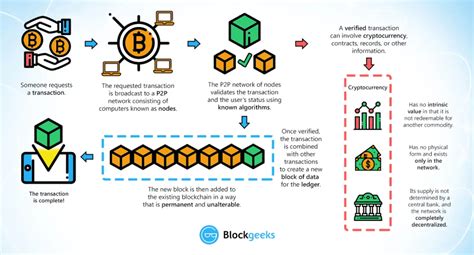
When the network experiences high levels of congestion due to increased activity on other blockchains or issues with smart contract execution, the block miner may choose to include only one transaction to avoid further delays or fees.
Observations from blockchain.info
On the Ethereum blockchain information platform, you can find a block with only one transaction (the mining reward) as follows:
This block is a reference point for observing unusual behavior on the network. It is essential to note that this specific block does not necessarily indicate an underlying problem with the Ethereum protocol or the blockchain itself.
Conclusion
The occurrence of a single transaction in a block is relatively rare and serves as an interesting case study in how the Ethereum network is designed to balance complexity with efficiency. While it may seem counterintuitive for a block to contain only one transaction, understanding the underlying reasons behind this phenomenon provides valuable insights into the workings of the Ethereum blockchain.
By observing these cases, developers, researchers, and users can gain a deeper understanding of the intricate mechanisms that govern the network and make informed decisions about its behavior in various scenarios.